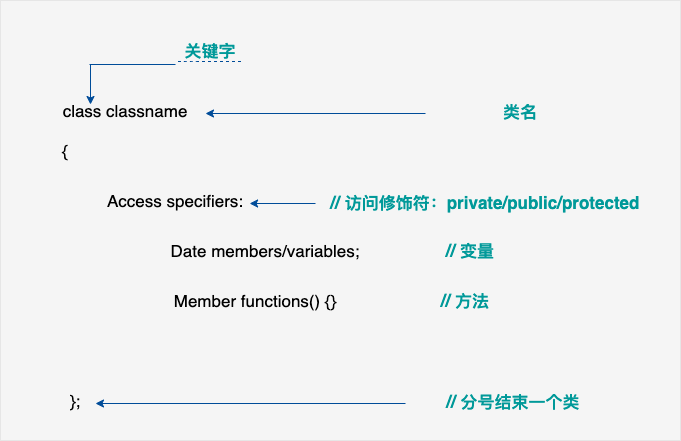
C++ 类 & 对象
![https://www.runoob.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/cpp-classes-objects-2020-12-10-11.png https://www.runoob.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/cpp-classes-objects-2020-12-10-11.png]()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
double length; // 长度
double breadth; // 宽度
double height; // 高度
// 成员函数声明
double get(void);
void set( double len, double bre, double hei );
};
// 成员函数定义
double Box::get(void)
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
void Box::set( double len, double bre, double hei)
{
length = len;
breadth = bre;
height = hei;
}
int main( )
{
Box Box1; // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box
Box Box2; // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box
Box Box3; // 声明 Box3,类型为 Box
double volume = 0.0; // 用于存储体积
// box 1 详述
Box1.height = 5.0;
Box1.length = 6.0;
Box1.breadth = 7.0;
// box 2 详述
Box2.height = 10.0;
Box2.length = 12.0;
Box2.breadth = 13.0;
// box 1 的体积
volume = Box1.height * Box1.length * Box1.breadth;
cout << "Box1 的体积:" << volume <<endl;
// box 2 的体积
volume = Box2.height * Box2.length * Box2.breadth;
cout << "Box2 的体积:" << volume <<endl;
// box 3 详述
Box3.set(16.0, 8.0, 12.0);
volume = Box3.get();
cout << "Box3 的体积:" << volume <<endl;
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Box1 的体积:210
Box2 的体积:1560
Box3 的体积:1536
- 私有的成员和受保护的成员不能使用直接成员访问运算符 (.) 来直接访问。
类 & 对象详解
| 概念 |
描述 |
| 类成员函数 |
类的成员函数是指那些把定义和原型写在类定义内部的函数,就像类定义中的其他变量一样。 |
| 类访问修饰符 |
类成员可以被定义为 public、private 或 protected。默认情况下是定义为 private。 |
| 构造函数 & 析构函数 |
类的构造函数是一种特殊的函数,在创建一个新的对象时调用。类的析构函数也是一种特殊的函数,在删除所创建的对象时调用。 |
| C++ 拷贝构造函数 |
拷贝构造函数,是一种特殊的构造函数,它在创建对象时,是使用同一类中之前创建的对象来初始化新创建的对象。 |
| C++ 友元函数 |
友元函数可以访问类的 private 和 protected 成员。 |
| C++ 内联函数 |
通过内联函数,编译器试图在调用函数的地方扩展函数体中的代码。 |
| C++ 中的 this 指针 |
每个对象都有一个特殊的指针 this,它指向对象本身。 |
| C++ 中指向类的指针 |
指向类的指针方式如同指向结构的指针。实际上,类可以看成是一个带有函数的结构。 |
| C++ 类的静态成员 |
类的数据成员和函数成员都可以被声明为静态的。 |
C++ 类成员函数
C++ 类访问修饰符
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Base {
public:
// 公有成员
protected:
// 受保护成员
private:
// 私有成员
};
|
公有(public)成员
公有成员在程序中类的外部是可访问的。您可以不使用任何成员函数来设置和获取公有变量的值
私有(private)成员
私有成员变量或函数在类的外部是不可访问的,甚至是不可查看的。只有类和友元函数可以访问私有成员。
默认情况下,类的所有成员都是私有的。
protected(受保护)成员
protected(受保护)成员变量或函数与私有成员十分相似,但有一点不同,protected(受保护)成员在派生类(即子类)中是可访问的。
继承中的特点
有public, protected, private三种继承方式,它们相应地改变了基类成员的访问属性。
- public 继承:基类 public 成员,protected 成员,private 成员的访问属性在派生类中分别变成:public, protected, private
- protected 继承:基类 public 成员,protected 成员,private 成员的访问属性在派生类中分别变成:protected, protected, private
- private 继承:基类 public 成员,protected 成员,private 成员的访问属性在派生类中分别变成:private, private, private
但无论哪种继承方式,上面两点都没有改变:
- private 成员只能被本类成员(类内)和友元访问,不能被派生类访问;
- protected 成员可以被派生类访问。
类构造函数 & 析构函数
类的构造函数
构造函数的名称与类的名称是完全相同的,并且不会返回任何类型,也不会返回 void。构造函数可用于为某些成员变量设置初始值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Line
{
public:
void setLength( double len );
double getLength( void );
Line(); // 这是构造函数
private:
double length;
};
// 成员函数定义,包括构造函数
Line::Line(void)
{
cout << "Object is being created" << endl;
}
void Line::setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
double Line::getLength( void )
{
return length;
}
// 程序的主函数
int main( )
{
Line line;
// 设置长度
line.setLength(6.0);
cout << "Length of line : " << line.getLength() <<endl;
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Object is being created
Length of line : 6
带参数的构造函数
默认的构造函数没有任何参数,但如果需要,构造函数也可以带有参数。这样在创建对象时就会给对象赋初始值,如下面的例子所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Line
{
public:
void setLength( double len );
double getLength( void );
Line(double len); // 这是构造函数
private:
double length;
};
// 成员函数定义,包括构造函数
Line::Line( double len)
{
cout << "Object is being created, length = " << len << endl;
length = len;
}
void Line::setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
double Line::getLength( void )
{
return length;
}
// 程序的主函数
int main( )
{
Line line(10.0);
// 获取默认设置的长度
cout << "Length of line : " << line.getLength() <<endl;
// 再次设置长度
line.setLength(6.0);
cout << "Length of line : " << line.getLength() <<endl;
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Object is being created, length = 10
Length of line : 10
Length of line : 6
使用初始化列表来初始化字段
1
2
3
4
|
Line::Line( double len): length(len)
{
cout << "Object is being created, length = " << len << endl;
}
|
上面的语法等同于如下语法:
1
2
3
4
5
|
Line::Line( double len)
{
length = len;
cout << "Object is being created, length = " << len << endl;
}
|
假设有一个类 C,具有多个字段 X、Y、Z 等需要进行初始化,同理地,您可以使用上面的语法,只需要在不同的字段使用逗号进行分隔,如下所示:
1
2
3
4
|
C::C( double a, double b, double c): X(a), Y(b), Z(c)
{
....
}
|
类的析构函数
类的析构函数是类的一种特殊的成员函数,它会在每次删除所创建的对象时执行。
析构函数的名称与类的名称是完全相同的,只是在前面加了个波浪号(~)作为前缀,它不会返回任何值,也不能带有任何参数。析构函数有助于在跳出程序(比如关闭文件、释放内存等)前释放资源。
下面的实例有助于更好地理解析构函数的概念:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Line
{
public:
void setLength( double len );
double getLength( void );
Line(); // 这是构造函数声明
~Line(); // 这是析构函数声明
private:
double length;
};
// 成员函数定义,包括构造函数
Line::Line(void)
{
cout << "Object is being created" << endl;
}
Line::~Line(void)
{
cout << "Object is being deleted" << endl;
}
void Line::setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
double Line::getLength( void )
{
return length;
}
// 程序的主函数
int main( )
{
Line line;
// 设置长度
line.setLength(6.0);
cout << "Length of line : " << line.getLength() <<endl;
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Object is being created
Length of line : 6
Object is being deleted
C++ 拷贝构造函数
拷贝构造函数是一种特殊的构造函数,它在创建对象时,是使用同一类中之前创建的对象来初始化新创建的对象。拷贝构造函数通常用于:
- 通过使用另一个同类型的对象来初始化新创建的对象。
- 复制对象把它作为参数传递给函数。
- 复制对象,并从函数返回这个对象。
1
2
3
4
5
|
classname (const classname &obj) {
// 构造函数的主体
//obj 是一个对象引用,该对象是用于初始化另一个对象的。
}
|
实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Line
{
public:
int getLength( void );
Line( int len ); // 简单的构造函数
Line( const Line &obj); // 拷贝构造函数
~Line(); // 析构函数
private:
int *ptr;
};
// 成员函数定义,包括构造函数
Line::Line(int len)
{
cout << "调用构造函数" << endl;
// 为指针分配内存
ptr = new int;
*ptr = len;
}
Line::Line(const Line &obj)
{
cout << "调用拷贝构造函数并为指针 ptr 分配内存" << endl;
ptr = new int;
*ptr = *obj.ptr; // 拷贝值
}
Line::~Line(void)
{
cout << "释放内存" << endl;
delete ptr;
}
int Line::getLength( void )
{
return *ptr;
}
void display(Line obj)
{
cout << "line 大小 : " << obj.getLength() <<endl;
}
// 程序的主函数
int main( )
{
Line line(10);
display(line);
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
调用构造函数
调用拷贝构造函数并为指针 ptr 分配内存
line 大小 : 10
释放内存
释放内存
下面的实例对上面的实例稍作修改,通过使用已有的同类型的对象来初始化新创建的对象:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Line
{
public:
int getLength( void );
Line( int len ); // 简单的构造函数
Line( const Line &obj); // 拷贝构造函数
~Line(); // 析构函数
private:
int *ptr;
};
// 成员函数定义,包括构造函数
Line::Line(int len)
{
cout << "调用构造函数" << endl;
// 为指针分配内存
ptr = new int;
*ptr = len;
}
Line::Line(const Line &obj)
{
cout << "调用拷贝构造函数并为指针 ptr 分配内存" << endl;
ptr = new int;
*ptr = *obj.ptr; // 拷贝值
}
Line::~Line(void)
{
cout << "释放内存" << endl;
delete ptr;
}
int Line::getLength( void )
{
return *ptr;
}
void display(Line obj)
{
cout << "line 大小 : " << obj.getLength() <<endl;
}
// 程序的主函数
int main( )
{
Line line1(10);
Line line2 = line1; // 这里也调用了拷贝构造函数
display(line1);
display(line2);
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
调用构造函数
调用拷贝构造函数并为指针 ptr 分配内存
调用拷贝构造函数并为指针 ptr 分配内存
line 大小 : 10
释放内存
调用拷贝构造函数并为指针 ptr 分配内存
line 大小 : 10
释放内存
释放内存
释放内存
C++ 友元函数
如果要声明函数为一个类的友元,需要在类定义中该函数原型前使用关键字 friend,如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class Box
{
double width;
public:
double length;
friend void printWidth( Box box );
void setWidth( double wid );
};
|
声明类 ClassTwo 的所有成员函数作为类 ClassOne 的友元,需要在类 ClassOne 的定义中放置如下声明:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
double width;
public:
friend void printWidth( Box box );
void setWidth( double wid );
};
// 成员函数定义
void Box::setWidth( double wid )
{
width = wid;
}
// 请注意:printWidth() 不是任何类的成员函数
void printWidth( Box box )
{
/* 因为 printWidth() 是 Box 的友元,它可以直接访问该类的任何成员 */
cout << "Width of box : " << box.width <<endl;
}
// 程序的主函数
int main( )
{
Box box;
// 使用成员函数设置宽度
box.setWidth(10.0);
// 使用友元函数输出宽度
printWidth( box );
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
C++ 内联函数
如果想把一个函数定义为内联函数,则需要在函数名前面放置关键字 inline,在调用函数之前需要对函数进行定义。如果已定义的函数多于一行,编译器会忽略 inline 限定符。
在类定义中的定义的函数都是内联函数,即使没有使用 inline 说明符。
下面是一个实例,使用内联函数来返回两个数中的最大值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
inline int Max(int x, int y)
{
return (x > y)? x : y;
}
// 程序的主函数
int main( )
{
cout << "Max (20,10): " << Max(20,10) << endl;
cout << "Max (0,200): " << Max(0,200) << endl;
cout << "Max (100,1010): " << Max(100,1010) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Max (20,10): 20
Max (0,200): 200
Max (100,1010): 1010
C++ this 指针
友元函数没有 this 指针,因为友元不是类的成员。只有成员函数才有 this 指针。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
// 构造函数定义
Box(double l=2.0, double b=2.0, double h=2.0)
{
cout <<"Constructor called." << endl;
length = l;
breadth = b;
height = h;
}
double Volume()
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
int compare(Box box)
{
return this->Volume() > box.Volume();
}
private:
double length; // Length of a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
};
int main(void)
{
Box Box1(3.3, 1.2, 1.5); // Declare box1
Box Box2(8.5, 6.0, 2.0); // Declare box2
if(Box1.compare(Box2))
{
cout << "Box2 is smaller than Box1" <<endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Box2 is equal to or larger than Box1" <<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Constructor called.
Constructor called.
Box2 is equal to or larger than Box1
C++ 指向类的指针
一个指向 C++ 类的指针与指向结构的指针类似,访问指向类的指针的成员,需要使用成员访问运算符 ->,就像访问指向结构的指针一样。与所有的指针一样,您必须在使用指针之前,对指针进行初始化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
// 构造函数定义
Box(double l=2.0, double b=2.0, double h=2.0)
{
cout <<"Constructor called." << endl;
length = l;
breadth = b;
height = h;
}
double Volume()
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
private:
double length; // Length of a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
};
int main(void)
{
Box Box1(3.3, 1.2, 1.5); // Declare box1
Box Box2(8.5, 6.0, 2.0); // Declare box2
Box *ptrBox; // Declare pointer to a class.
// 保存第一个对象的地址
ptrBox = &Box1;
// 现在尝试使用成员访问运算符来访问成员
cout << "Volume of Box1: " << ptrBox->Volume() << endl;
// 保存第二个对象的地址
ptrBox = &Box2;
// 现在尝试使用成员访问运算符来访问成员
cout << "Volume of Box2: " << ptrBox->Volume() << endl;
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Constructor called.
Constructor called.
Volume of Box1: 5.94
Volume of Box2: 102
C++ 类的静态成员
![https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/xinqinew/pic@main/img/08131CEC-4FF2-4E14-818D-1FB5ED410C75.png https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/xinqinew/pic@main/img/08131CEC-4FF2-4E14-818D-1FB5ED410C75.png]()
不能把静态成员的初始化放置在类的定义中,但是可以在类的外部通过使用范围解析运算符 :: 来重新声明静态变量从而对它进行初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
static int objectCount;
// 构造函数定义
Box(double l=2.0, double b=2.0, double h=2.0)
{
cout <<"Constructor called." << endl;
length = l;
breadth = b;
height = h;
// 每次创建对象时增加 1
objectCount++;
}
double Volume()
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
private:
double length; // 长度
double breadth; // 宽度
double height; // 高度
};
// 初始化类 Box 的静态成员
int Box::objectCount = 0;
int main(void)
{
Box Box1(3.3, 1.2, 1.5); // 声明 box1
Box Box2(8.5, 6.0, 2.0); // 声明 box2
// 输出对象的总数
cout << "Total objects: " << Box::objectCount << endl;
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Constructor called.
Constructor called.
Total objects: 2
静态成员函数
静态函数只要使用类名加范围解析运算符 :: 就可以访问。
静态成员函数只能访问静态成员数据、其他静态成员函数和类外部的其他函数。
静态成员函数与普通成员函数的区别:
- 静态成员函数没有 this 指针,只能访问静态成员(包括静态成员变量和静态成员函数)。
- 普通成员函数有 this 指针,可以访问类中的任意成员;而静态成员函数没有 this 指针。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
static int objectCount;
// 构造函数定义
Box(double l=2.0, double b=2.0, double h=2.0)
{
cout <<"Constructor called." << endl;
length = l;
breadth = b;
height = h;
// 每次创建对象时增加 1
objectCount++;
}
double Volume()
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
static int getCount()
{
return objectCount;
}
private:
double length; // 长度
double breadth; // 宽度
double height; // 高度
};
// 初始化类 Box 的静态成员
int Box::objectCount = 0;
int main(void)
{
// 在创建对象之前输出对象的总数
cout << "Inital Stage Count: " << Box::getCount() << endl;
Box Box1(3.3, 1.2, 1.5); // 声明 box1
Box Box2(8.5, 6.0, 2.0); // 声明 box2
// 在创建对象之后输出对象的总数
cout << "Final Stage Count: " << Box::getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}
|
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Inital Stage Count: 0
Constructor called.
Constructor called.
Final Stage Count: 2